Radioactivity ICSE and CBSE Part 2
1st Part link is here .......... Part 1
Radioactivity Class 10 and 12 Notes Physics and Important question
Introduction
Radio isotopes are isotopes of elements which have atomic number less than 82 and are radioactive. They are prepared by nuclear transmutation. They have medicinal, scientific, and industrial uses.
Medicinal uses:
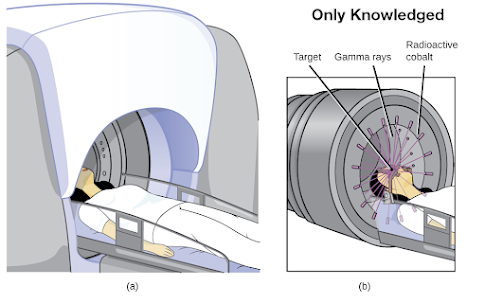
- Diseases like cancer and leukemia are cured by radio therapy. Gamma radiations by Cobalt-60 are used to cure cancer by killing the cells in the magligant tumor. The radiations need to penetrate through the human skin.
- Salts of weak radioactive isotopes like radio-sodium chloride, radio-iron, and radio-iodine are called tracers. They are used for detecting brain tumors and blood clots. It is also used to study the processes of the body. For example, radio-sodium chloride is used to study the blood circulation in the body and is called radio cardiology.
- Gamma rays are used to sterlize things like syringes, badges, dressings and other equipment. This method is method is more reliable than sterilization by heat.
Scientific uses:
- Alpha particles are used as projectiles for nuclear reactions. They are also used in estimation of the size of the nucleus of various elements.
- Tracers are used to study the processes of plant growth. For e.g. how much phosphate a plant takes in and to which part the phosphate goes.
- The age of old excavated materials is found by the rate of disintegration and smission of beta particles by C-14. This process is called carbon dating.
Industrial uses:
- U-235 can be used as a fuel for atomic energy reactors.
- Charge accumulated by the moving parts of machines due to friction are taken away by the ionised air due to radiations.
- The radiations help in making certain luminescent signs.
- Due to the penetrating powers of beta radiations, they can be used as a check on the thickness of paper, wood, metal, etc.
Sources of harmful radiation:
- Radioactive fallout from nuclear power plants: Nuclear power plants are major sources of electricity. If an accident occurs, the radioactive materials would be released and thrown into the atmosphere. it affects the people who work in the plants, the plant's infrastructure, the people in the vicinity and the places where the radioactive substances are transported by wind. Three major accidents are: 1. U.S.A. (28th March 1979), 2. Ukraine (26th April 1986) 3. Japan (11th March 2011).
- Nuclear waste: The fuel rod used in nuclear power plants decreases in power after many uses. They should not be dumped into open garbage or water bodies because they are still radioactive and affect human and animal life.
- Cosmic radiation and X-rays: Cosmic rays reach the Earth from sun and outer space. The charged particles may be deflected by the Earth's magnetic field and uncharged rays like gamma and X-rays come to the Earth are harmful for human beings. High energy accelerators also produce X-rays.
Harmful effects of radiation:
Radiotions interact with living tissue within 10-14 seconds and cause immense biological damage.
Biological effers of nuclear radiations are of three types:
- Short term recoverable affects: diarrhea, sore throat, loss of hair, nausea
- Long term irrecoverable effects: leukemia, cancer
- Genetic effects
The first two effects are seen in people constantly exposed to radiations by work. The third effect is seen in the offspring of such people. This happens due to mutation in genes.
The effects are acute in people exposes to bursting radiations in the reactors. It also affects people working in atomic energy establishments.
Exposure of a pregnant women to radiation causes 40% risk of cancer, 50% risk of tumor and 70% risk of leukemia. exposure to X-rays to upper body parts cause damage the thyroid glands and cause cancer.
Exposure to gamma radiations causes destructionof cells, blood cells, gastrointestinal track, reproductive cells, hair cells, DNA and RNA harms in cells, etc.
Safety precaustions while using nuclear energy:
Nuclear power plants are used to generate electricity. For this, the following aspects require care:
Establishment of Nuclear power plants
- People working in the power plants should not be exposed to radiation too much. There should be a minimum spread of radiations in accidents.
- The nuclear reactor should be shielded with lead or steel to stop radiations from getting outside.
- The reactor should be present in a strong, airtight concrete building which can withstand earthquakes, fires or explosions.
- The core of the nuclear power plant should have a backup cooling system so that it does not melt due to high temperature.
Handling of radioactive materials
- People working in power plants must put on lead gloves and lead lined aprons.
- handling of radioactive materials must be done with long lead tongs.
- Film badgest should be used to ensure that no person is exposed to radiations beyond the safe limit.
- The radioactive materials should be kept in lead boxes with a single narrow opening for usage. This helps to prevent rays from going out in all directions.
Safe disposal of nuclear waste:
Radioactive materials after use are called nuclear waste. They are obtained from laboratories, Hospitals and research centres. These wastes are still radioactive and must be put in thick casks. These burials or mines should be sealed completely. This is the proper way of disposing nuclear waste.Continuation Part 3 is here...........




0 Comments
Hope Everyone Reading my posts are gaining KNOWLEDGE and able to know something new and informative.
📚📖📕🧾📝😅
Sharing is Caring. So please share this website with everyone you know so that they can also improve their KNOWLEDGE !!!