ICSE Chemical Bonding and Important Notes and Question Part - 2
Chemical Bonding
Covalent compounds are polar when the shared pair of electrons between the two atoms are not equally shared between them. This results in fractional positive or negative charges on them and ionise in water.
For example, in hydrogen chloride, chlorine has more electronegativity than hydrogen. Chlorine attracts the shared pair of electrons towards itself and develops a slight negative charge. The hydrogen atom develops a slight positive charge.
In solution, the fractional charges in polar covalent compounds are converted to complete charges and ions are produced. This process is called ionisation.
The more the electronegativity difference between two atoms forming a bond, the more the polar nature of the molecule. Bonds formed between two atoms with same electronegativity is non-polar, of slightly different electronegativity is polar and of more difference in electronegativity is ionic.
A molecule that has both, slight positive and negative charge is called a dipole molecule.
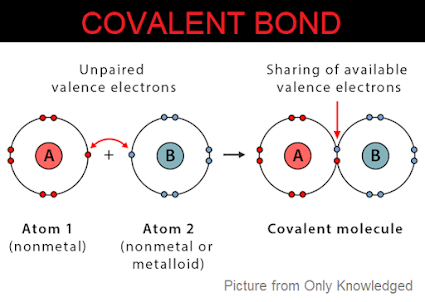
Conditions for the formation of a covalent bond:
- Both atoms should have four or more electrons in the valence shell.
- Both the atoms should have high electronegativity.
- Both the atoms should have high electron affinity.
- Both the atoms should have high ionisation energy.
- Both the atom’s electronegativity difference should be 0 or negligible.
Properties of electrovalent compounds:
- Their constituent particles are ions.
- They are hard solids because of the strong electrostatic force of attraction between the ions.
- They have high melting and boiling points due to the force of attraction between the ions.
- They do not conduct electricity in solid state.
- They become good conductors of electricity in fused or aqueous state.
- They disassociate into their respective ions when electricity is passed through them in molten or aqueous state.
- They are soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents.
- They react rapidly in chemical reactions in the aqueous state.
Properties of covalent compounds:
- Their constituent particles are molecules.
- They are gases, liquids or soft solids due to weak forces of attraction in their bonds.
- They have low melting and boiling points due to weak forces of attraction in the bond.
- They are poor conductors of electricity in molten or aqueous state.
- Non-polar covalent compounds do not ionise when electricity is passed through them. Polar compounds ionise in their solutions and act as an electrolyte. Disassociation of ions cannot take place.
- They are soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water.
- Their chemical reactions are slow in aqueous solutions.
Effect of electricity on electrovalent and covalent compounds:
Arrange an electric circuit having a 6-Volt battery, an ammeter and platinum electrodes connected in series.
Electrovalent compounds: Electrovalent compounds disassociate into ions and allow electricity to pass through them. Hence, the bulb glows. Ionic compounds are good conductors of electricity in molten or aqueous states due to free mobile electrons.
Covalent compounds: Covalent compounds do not disassociate into ions. They do not conduct electricity as they have only molecules and the bulb doesn’t glow.
Coordinate bond:
The bond formed between two atoms by sharing a pair of electrons, provided entirely by one of the combining atoms but shared by both is called a coordinate bond or dative bond.
Conditions of formation:
- One of the two atoms must have at least one lone pair of electrons. A pair of electrons which is not shared is known as the lone pair of electrons.
- The other atom should be short of at least a pair of electrons.
Coordinate covalent bonds are also called bonds formed between an ion and an atom of a polar covalent bond molecule with one or more lone pairs of electrons. They have properties of both covalent and ionic bonds and so, they are also called as dative or co-ionic bond.
The atom which donates the electron pair for the formation of a coordinate bond is called the donor and the atom sharing the donated electron pair is called the acceptor. Coordinate bonds are represented by an arrow sign.
Water molecules have 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom. It has two lone electron pairs. They repel the bond pairs between oxygen and hydrogen which results in the V-shaped structure of a water molecule. Hence, water is a polar compound.
When an acid is added to water, strong dipole interaction takes place between polar water molecules and polar acid molecules. Then, the hydrogen ions from acid molecules get released adds on to the lone pair electrons of water molecules forming a coordinate covalent bond. Thus, a hydronium ion is formed.
Hydronium ion has one lone pair of electrons, two covalent bonds and a coordinate bond.
In an ammonia molecule, a pair of lone electrons are present. It combines with hydrogen ion and is attracted towards the lone pair of electrons. The bond formed is a coordinate bond.
Ammonium chloride is a good example of a molecule having all types of bonds. Compounds having electrovalent and covalent compounds are sodium hydroxide and calcium carbonate. Compound having covalent and coordinate bond is sulphuric acid.
Hydroxyl or hydroxide ion is formed when a hydrogen ion is removed from water molecule. The lone pair of electrons remains with oxygen as it is more electronegative. Thus, hydroxide ion is negatively charged
When water molecules are ionised, it releases hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions. Hydrogen ion is transferred to the oxygen of other water molecules to form hydronium ions. Hydronium and hydroxide ions are both formed from water. This is called self-ionisation of water.




0 Comments
Hope Everyone Reading my posts are gaining KNOWLEDGE and able to know something new and informative.
📚📖📕🧾📝😅
Sharing is Caring. So please share this website with everyone you know so that they can also improve their KNOWLEDGE !!!