ICSE Chemical Bonding Important notes and Important Question
Chapter-2 Chemical Bonding
Atoms have to have a complete octet to be stable. Elements need electrons in the valence shell or two in case of hydrogen and helium to attain stability. For this, atoms donate, gain or share electrons to attain a stable electronic configuration.
Cause of chemical combination is the tendency of elements to acquire the nearest noble gas configuration in their valence shell and become stable.
The force of attraction between atoms in a molecule to hold them together is called a chemical bond.
A chemical bond is the force of attraction between any two atoms in a molecule to maintain their stability.
There are three ways in which an atom can attain stability:
- Transferring electrons to form an electrovalent or ionic bond
- Sharing electrons to form a covalent or molecular bond
- Sharing by only one atom in the bond called coordinate or dative bond
Electrovalent bond:
This bond is formed between metals and non-metals. All the atoms in the bond have the electronic configuration of the nearest inert gas. Metals form cations and non-metals form anions.
An ion is a charged particle that is formed due to the gain or loss of one or more electrons by an atom.
Metallic elements are electropositive and non-metallic elements are electronegative.
The cations and anions attract each other due to electrostatic force of attraction and form electrovalent or ionic bonds.
The chemical compounds formed as a result of the transfer of electrons from one atom of an element to one atom of another element are called ionic or electrovalent bonds.
The number of electrons that an atom loses or gains to form an electrovalent bond is its electrovalency.
Conditions for the formation of an electrovalent bond:
The formation of cations or anions from the neutral atom depends upon the following factors:
- Low ionisation potential: If the ionisation potential of an atom is low, it means that it can lose electrons easily to form a cation.
- High electron affinity: Due to high electron affinity, anions are easily formed.
- Large electronegativity difference: Transfer of electrons occur when the atoms of the two elements have a large electronegativity difference. This will increase the ionic nature of the compound.
Always, metals which have a tendency to lose electrons and non-metals which have the tendency to gain electrons to form ionic bonds.
Since the force of attraction by the opposite charges are higher, ionic compounds are very stable.
Electron dot symbol or Lewis symbol has the symbol of the element in the centre surrounded by only the valence electrons. Symbols like dots and crosses are used to distinguish the electrons gained or shared by the other atom.
In the formation of an electrovalent bond, the electropositive atom undergoes oxidation and the electronegative atom undergoes reduction. This process is called redox reaction.
Oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously because the electrons lost by an atom is gained by the other in an electrovalent bond.
An oxidising agent is an acceptor of electrons and a reducing agent is a donor of electrons.
The chemical bond formed between two combining atoms by mutual sharing of electrons is called a covalent or molecular bond and the compound formed is called a covalent compound.
This compound is formed between elements which do not favour the loss of electrons to attain an octet. Thus, each atom contributes an equal number of electrons and shares them by pairs to attain octets.
Covalent bonds can be formed by atoms of different elements or atoms of same element.
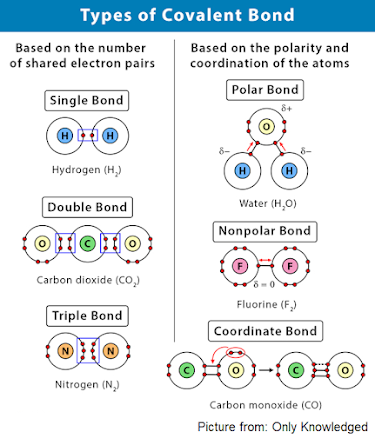
Covalent bonds are of three types:
- Single covalent bond: Formed when one pair of electrons are shared between the atoms. E.g. Molecules of hydrogen, chlorine, hydrogen chloride, water, methane, carbon tetrachloride, etc.
- Double covalent bond: Formed when two pairs of electrons are shared between the atoms. E.g. Molecules of oxygen, etc.
- Triple covalent bond: Formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the atoms. E.g. Molecules of nitrogen, etc.
Molecules can also be formed with the combination of single, double or triple covalent bonds. E.g. Ethene, Ethyne, etc.
The covalency of an atom is the number of electrons that take part in the formation of shared pairs. Covalency of hydrogen is 1, oxygen is 2, nitrogen is 3, and carbon is 4.
Covalent compounds are non-polar when the shared pair of electrons are equally distributed between the two atoms and the molecule is symmetrical and electrically neutral.
Molecules formed by the similar atoms attract the shared pair of electrons equally due to same electronegativity are non-polar. E.g. Hydrogen, Chlorine, Oxygen, etc. They do not ionise in water.
Molecules formed between dissimilar atoms can be non-polar if polarities are cancelled out in the bond. E.g. methane, carbon tetrachloride.




0 Comments
Hope Everyone Reading my posts are gaining KNOWLEDGE and able to know something new and informative.
📚📖📕🧾📝😅
Sharing is Caring. So please share this website with everyone you know so that they can also improve their KNOWLEDGE !!!