Transpiration, Guttation, bleeding | Important MCQS question for ICSE and CBSE
Transpiration,
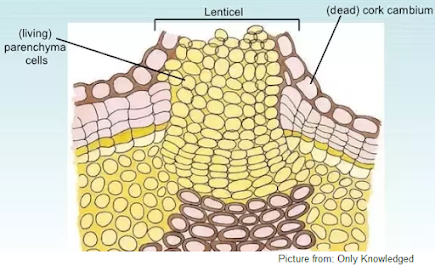
Lenticular transpiration:
Lenticels are openings with are found only in thick and old barks of plants and trees. They allow diffusion and exchange of gases. They remain open all the time and contributes to transpiration. The amount of transpiration is more than in lenticels and less than in stomata.
Factors affecting transpiration:
A. Internal factors:
- Sunlight: The amount of transpiration increases with the increase in sunlight (heat).
- Temperature: Increase in temperature increases the rate of transpiration.
- Wind velocity: Increase in wind velocity increases the rate of transpiration as it moves water vapour creating space for more water vapour to take its place.
- Humidity: Transpiration is reduced with the increase in humidity of the atmosphere.
- Carbon dioxide: Increase in carbon dioxide level in atmosphere above 0.03% results in closure of stomata and transpiration is reduced.
- Atmospheric pressure: The rate of transpiration increases with the decrease in atmospheric pressure.
B. Internal factor:
When the water content in the leaves decrease, transpiration stops as the guard cells become flaccid. This is a natural mechanism by the leaves to prevent transpiration.
Adaptations by the plants to reduce transpiration:
- Sunken stomata: Stomata are sunken or covered with hair (Nerium) to prevent excess transpiration.
- The amount of stomata in the leaves is reduced.
- The leaves may be narrower to reduce surface area.
- Leaves may be shed or modified to spines to reduce transpiration.
- Thick cuticles in the leaf surfaces also reduce transpiration.
Significance of transpiration:
- Cooling effect: Transpiration is necessary for cooling down the leaf as excess heat destroys enzymes.
- Suction force: Transpiration helps to create suction force which helps in the ascent of water and minerals upwards the stem.
- Transpiration helps in the process of upwards conduction of water and minerals through the stem.
Transpiration in plants is not an excretory process.
Transpiration affects climate:
Due to transpiration, large amounts are water are transpired into the atmosphere. This helps to bring rain. This is how forests bring rain.
Differences between evaporation and transpiration:
- Evaporation is the process of loss of water from water bodies whereas transpiration is the process of loss of water from the aerial parts of the plant.
- Evaporation is affected by temperature and humidity of the atmosphere whereas transpiration is affected by internal and external factors of the plant.
- Evaporation is a fast process whereas transpiration is a slow process.
Guttation and bleeding:
Some plants lose water along with dissolved minerals not as water vapour but as water droplets. This process is called exudation and the fluid is called exudation which can occur in two ways: guttation or bleeding.
Guttation: It is the process of removal of water droplets through hydathodes in the margins of leaves of plants growing in warm and humid conditions during mornings. It created a hydrostatic force inside the plant and is common in banana, nasturtium, and strawberry.
Bleeding: It is the process of removal of sap of the plant due to injury from the ruptured or cut surface and is assisted by the root pressure.
Differences between guttation and bleeding:
- Guttation occurs through hydathodes normally whereas bleeding occurs through ruptured or cut surfaces in injured plants.
- In guttation, the exudate is mainly water with dissolved salts whereas in bleeding, the exudate is mainly sap and sugars.
- Guttation occurs during early mornings and late nights whereas bleeding occurs whenever a plant is injured.
- Guttation occurs in plants like banana, nasturtium and strawberry whereas bleeding occurs in all plants.
Differences between transpiration and guttation:
- In transpiration, water is lost as water vapor whereas in guttation, water is lost as water droplets.
- In transpiration, water is lost in pure form whereas in guttation, water is lost along with dissolved minerals.
- Transpiration occurs through stomata, lenticels, and cuticles whereas guttation occurs through hydathodes.
- Transpiration can cause loss of turgidity in leaf whereas guttation has no effect on the turgidity of the leaf.
- Transpiration is regulated by the guard cells whereas guttation cannot be regulated.
- Transpiration occurs in the presence of sunlight whereas guttation occurs at early mornings and late nights.
- Transpiration cools down the plant whereas guttation does not have a cooling effect.
- Transpiration occurs in dry conditions whereas guttation occurs in humid conditions.



0 Comments
Hope Everyone Reading my posts are gaining KNOWLEDGE and able to know something new and informative.
📚📖📕🧾📝😅
Sharing is Caring. So please share this website with everyone you know so that they can also improve their KNOWLEDGE !!!